EVS Client
EVSClient - Installation & Configuration
External Validation Service Front-end (Aka EVSClient) is an open-source Java EE project used to present a unified interface for calling various validation-services of e-Health standards.
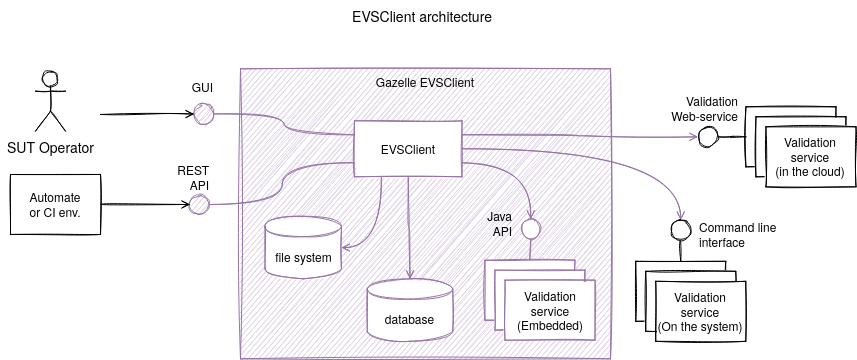
Validation services can be web-services, other application deployed on the machine and accessible with CLI or JARs embedded in EVSClient EAR. Except for embedded JARs, EVSClient does not provide those validation-services. They must be installed otherwise.
Get EVSClient
Build from sources
Sources of this project are available on the INRIA GitLab; sources are managed using git. Anonymous access is available if you only want to retrieve the sources (read-only access). If you intend to build the tool and to install it on your own server, we recommend you to use a tagged version.
git clone --branch "TAG_VERSION" https://gitlab.inria.fr/gazelle/applications/test-execution/validator/EVSClient.git
To retrieve the current version of the tool, take a look into the release notes of the project in Jira .
Despite sources being and running with Java 7, the project needs JDK 8 and Maven to be compiled (this is related to Sonar analysis).
mvn clean install
Once the compilation is over, the deployable artifact can be found in EVSClient-ear/target/evs.ear.
Or download the EAR from IHE artifact repository
Each version of EVSClient is published in IHE Gazelle Nexus repository.
EVSClient-ear-X.X.X.ear is the artifact to download and deploy.
Installation
Pre-requisites
EVSClient requires Debian or Ubuntu, JDK 7, JBoss AS 7.2.0-Final and PostgreSQL to be run (even though it is build with JDK 8). Please refere to General considerations for JBoss 7 to install JBoss 7 and setup a compliant environment.
Create and initialize the database
Since version 6.1.0, database and schema are created automatically by FlywayDB during deployment.
However, you still need to create the database and the user.
This initialization is done by the scripts in EVSClient-ejb/src/main/resources/db/baseline/:
schema.sql.init.sql.
For more information about FlywayDB, please refer to the documentation.
Note: Initial application preferences values (application_url, cas_enabled, …) should be provided as environment variables.
Default values could be found in /opt/evs/preferences.properties.</br>
If any of these variables is set, the corresponding preference in preferences.properties file will be overridden.
Data source
Since version 5.11.1, data sources (configuration file that indicates how to connect to the database) must be defined in the JBoss application server. More information about how to configure data sources can be found here: JBoss7 datasources.
EVSClient will expect the JNDI datasource to be named: java:jboss/datasources/EVSClientDS.
A data source example and specific to EVSClient can be found in EVSClient-ear/src/main/datasource
in the sources or in the archive EVSClient-ear-X.X.X-datasource.zip that can be downloaded from
https://gazelle.ihe.net/nexus.
File system
EVSClient will store user files and validation-reports on the file system of the machine in specific directories.
By convention, EVSClient store all files at /opt/evs, but this can be changed in the
application preferences.
A ZIP file is available at https://gazelle.ihe.net/nexus/#nexus-search;quick~EVSClient (search for the last released EVSClient-ear-X.X.X-dist.zip) that you can unzip in order to easily create all the required directories, starting at /opt.
wget -nv -O /tmp/EVSClient-dist.zip "[*https://gazelle.ihe.net/nexus/service/local/repositories/releases/content/net/ihe/gazelle/EVSClient-ear/6.X.X/EVSClient-ear-6.X.X-dist.zip*](https://gazelle.ihe.net/nexus/service/local/repositories/releases/content/net/ihe/gazelle/EVSClient-ear/6.X.X/EVSClient-ear-6.X.X-dist.zip)"
unzip /tmp/EVSClient-dist.zip -d /
Single Sign On Installation
SSO installation is optional.
Since version 5.13.0, EVSClient needs a file to be integrated with the Gazelle SSO application.
An instance of Gazelle SSO must be deployed, the file evs.properties
shall be in /opt/gazelle/cas and must contain the following statements :
casServerUrlPrefix=https://<yourfqdn>/sso
casServerLoginUrl=https://<yourfqdn>/sso/login
casLogoutUrl=https://<yourfqdn>/sso/logout
service=https://<yourfqdn>/evs
IP address geographic location configuration.
IP geographic location is optional.
EVSClient embbed an IP geographic location feature that collect countries of calling IP address and display a world map of anonymized validation requests.
The country computing is performed by the third service https://api.ipgeolocation.io/.
The certificate of this service must be installed in the truststore of the JBoss running EVSClient. To get the certificate of the service, open https://api.ipgeolocation.io/ with your browser and download the certificate by clicking on the padlock.

Then add the certificate into the truststore.
sudo keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias ipgeolocation -file ipgeolocation.crt -keystore /opt/gazelle/cert/truststore.jks
The truststore path must be the path referenced in /etc/init.d/jboss7, in the option OPT_SSL and -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore.
Deployment
Once you have retrieved the archive (see Get EVSClient), copy it to your JBoss7
server in the ${JBOSS_DIR}/standalone/deployments directory. The EAR copied in this folder MUST be
named evs.ear.
cp EVSClient-ear-X.X.X.ear /usr/local/jboss7/standalone/deployments/evs.ear
sudo service jboss7 start
If you did not change any default configuration, EVSClient should be accessible at http://localhost:8080/evs.
Upgrading an existing installation
The database is updated with the migration scripts located in EVSClient-ear/src/main/resources/db/migration.
The migration scripts are executed automatically by FlywayDB during deployment.
WARNING The upgrade procedure has changed overtime, and some version requires specific actions, see Specific updates.
In the following procedures, the term “intermediate version” is used and means all released version between the one currently installed and the one targeted for the update. For example if you are running EVSClient 5.13.0 and want to update to the 5.13.4, intermediate versiond are 5.13.1, 5.13.2 and 5.13.3.
Procedure before version 6.0.0
EVSClient was automatically but partially updating the database schema. This partial migration required to do the following steps
- Backup the database and the
/opt/EVSClient_proddirectory. - deploy the next version EVSClient of the one currently deployed (no jump of versions are allowed or you may end up with corrupted data).
- Wait for the database to be updated automatically (i.e. EVSClient completely started).
- Then stop EVSClient
- run the SQL
update-X.X.X.sqland/orupdate-X.X.X.shscripts if they exists (with X.X.X being the version deployed)# Run SQL script psql -U gazelle evsclient < update-X.X.X.sql # And/or run shell script chmod +x update-X.X.X.sh ./update-X.X.X.sh - and finally restart EVSClient.
- Repeat from step 2 to 6 for every intermediate version up to the target one.
Update procedure since version 6.0.0
Due to too many mistakes in the update procedure, but also to simplify automated installation, the data migration has been entirely been delegated to the scripts. This procedure only apply if EVS 6.0.0-RC3 or newer is already installed.
- Backup the database and the
/opt/evsdirectory. - run ALL
update-X.X.X.sqland/orupdate-X.X.X.shscripts of every intermediate versions up to the target version (if they exists). - Deploy and start the targeted EVSClient version.
Update procedure since version 6.1.0
If you are using the 6.1.0 version or newer, you will not find any update-X.X.X.sql or update-X.X.X.sh.
The migration scripts are now embedded in the EVSClient EAR and are executed automatically by FlywayDB.
Specific updates
5.11.1 The datasource has been externalized from the EAR and must be configured in JBoss. See Data source.
5.13.0 The SSO configuration file has changed. It does not use
/opt/gazelle/cas/file.properties anymore, but /opt/gazelle/cas/EVSClient.properties. See
Single Sign On Configuration.
6.0.0 No data migration is possible from EVSClient 5.x.x to 6.x.x. The database has changed
a lot, and we did not provide the script (feel free to contribute if required). Also update scripts
for version 5.x.x and older are no more available in the released sql.zip archive. However, if it is
required to keep archived data of previous validation, it is possible to deploy EVSClient 6.x.x
while keeping an old EVS 5.x.x running in read-only mode. See
EVSClient setup to keep EVS 5.x.x legacy data.
Also application URL path changed from /EVSClient to /evs, SSO file change from
/opt/gazelle/cas/EVSClient.properties to /opt/gazelle/cas/evs.properties.
Troubleshooting
Unable to reach EVSClient
If you have issue reaching the application, you may need to change the application URL directly from the database.
# Connect to the database server in CLI
psql -U gazelle evsclient
-- Update application URL to your domain --
update cmn_application_preference
set preference_value = 'http://localhost:8080/evs'
where preference_name = 'application_url';
Troubles login into EVSClient
If you have issue authentifying you to the application, you may need to temporarly disable the SSO to access to the configuration of the preferences of the application.
Those SQL commands will switch EVSCLient into IP Login mode (See Authentication).
# Connect to the database server in CLI
psql -U gazelle evsclient
update cmn_application_preference
set preference_value = 'false'
where preference_name = 'cas_enabled';
update cmn_application_preference
set preference_value = 'true'
where preference_name = 'ip_login';
update cmn_application_preference
set preference_value = '.*'
where preference_name = 'ip_login_admin';
Administration manual
The following elements of EVSClient can be administrated:
- The application preferences use to enable or disable certain modes and customize EVSClient behavior,
- the validation-services available,
- references to standards or integration-profiles related to the validations,
- the top menu bar and
- “calling” tools able to forwards messages or documents to EVSClient for validation and might query the EVSClient for the result.
Application preferences
Users with admin\_role role can access the application preferences section through the menu
Administration –> Manage application preferences.

- Preference Key is a one word (no space) key to identify the preference
- Class is the name of the java type used by the application to understand the preference.
Possible values are (list is indicative and not exhaustive):
- java.lang.String
- java.lang.Integer
- java.lang.Boolean
- Preference Value is the value of the preference
- Description is a text describing the purpose of the preference
The button Create Missing Preference creates some preferences that the application needs to run The button Set default http headers values set the value of the preferences that are needed to set the http header of the pages served by the application to the default value for a good level of security of the application. The button Reset Resteasy cache is used to the reset the values cached by the application for serving rest requests.
Click on the edit button in order to edit an existing preference
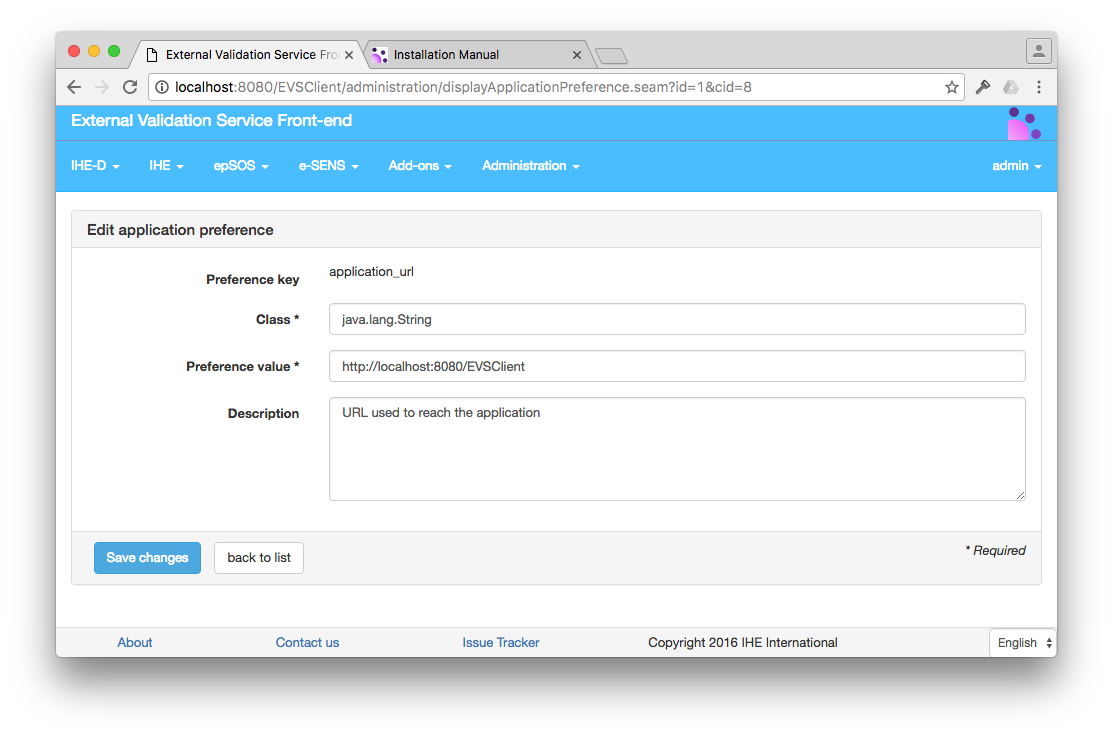
Preferences are put in a cache, so in order to take modification into account, EVSClient must be restarted.
touch /usr/local/jboss7/standalone/deployments/evs.ear
It is also possible to add a new preference by clicking on the green button
“Create new application preference”. This should not be required if all migration-scripts are
correctly run during application upgrades.

Authentication
There is no user registry in EVSClient. EVSClient is either configured to get authentication token from a Single-Sign-On service (Apereo CAS) either configured to grant admin rights based on IP address filtering.
CAS Configuration
When Central Authentication Service (CAS) is enabled, users identity and roles are provided by Gazelle SSO.
To enable the CAS:
- Preference
cas_enabledmust be set totrue, - preference
ip_loginmust be set tofalse, - property file gathering SSO URLs information must be installed. See Single-Sign-On Installation.
IP Login
WARNING, except on an isolated or secured local network, IP Login is a degraded and unsecure mode and should only be limited to the installation or testing of EVSClient.
If CAS is not available, there is a degraded mode using an IP address based login. If this mode is activated, a click on the login button of the application menu bar will grant the role admin to all users which have an IP address that matches the defined regular-expression.
To enable IP Login:
- Preference
cas_enabledmust be set tofalse, - preference
ip_loginmust be set totrue, - preference
ip_login_adminmust be defined with a regular-expression.*any visitor can be granted admin192\.168\..*any visitor from the network 192.168.. can be granted admin, etc.
Validation services
Validation services are components that actually performs the validation of documents, whereas EVSClient is “just” a facade and a dispatcher. A validation service can either be a web-service, a binary executed on the server or either a JAR library embedded in EVSClient EAR.
Going to Administration –> Manage validation services, the administrator will access the list of all the validation services which are declared and used by the application. Each entry can be edited. Administrator of the application can also create new entries, in order to declare new validation services

Add or edit a validation service
Click on the button “Create new validation service” in order to acces the form to create a new service entry in EVSClient, or click on the pencil at the end of each validation-service row to edit an existing entry.
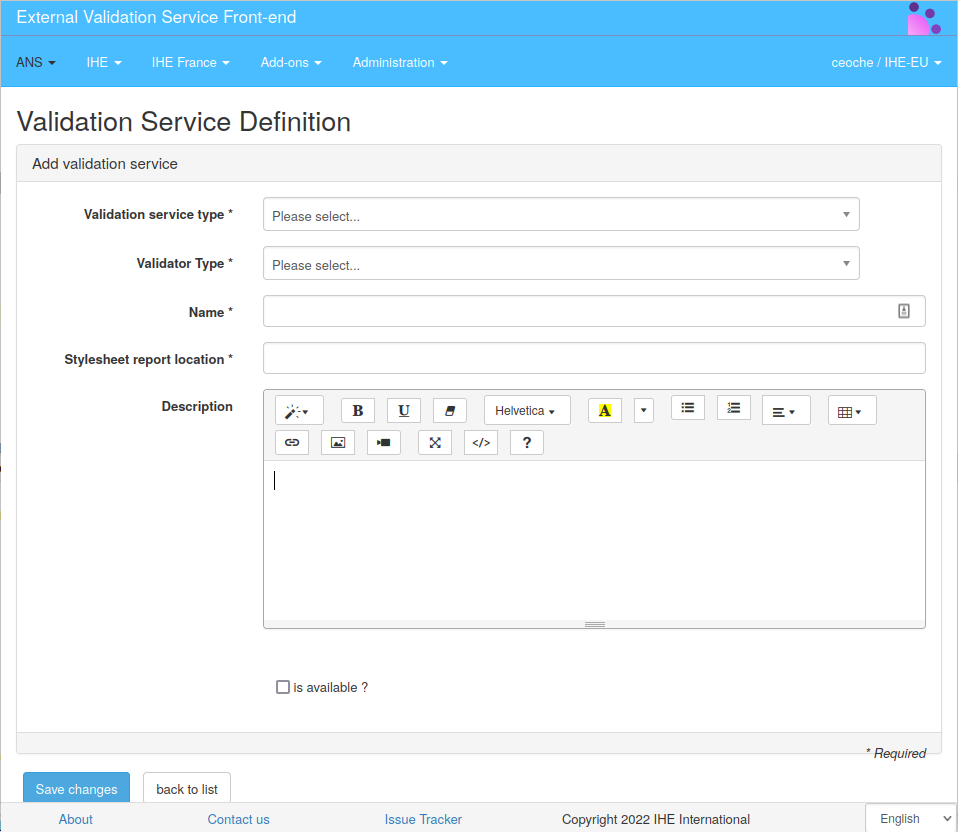
When defining a validation service, the following elements should be provided:
- Validation Service Type defines the client type required to contact the validation-service (required).
- Validation Type is a legacy way to categorize validation reports in the persistence storage
(required). As example HL7v2 type will relate to
hl7v2_repositorypath in application-preferences. - Name is the unique name of the service in this EVS instance (required).
- Stylesheet report location is the link to the XSL to be used to display validation reports returned by this validation-service (required).
- Description is a field to provide documentation or information about the service. It will be displayed to the user in validation GUI.
- Specific to Web services type
- Target endpoint Define the complete URL to the web-service endpoint (required). For example
https://gazelle.ihe.net/XDStarClient-ejb/ModelBasedValidationWSService/ModelBasedValidationWS?wsdl. Note that?wsdlis expected at the end of the URL for SOAP web-services. - Support compression ? Enable/disable ZIP compression when exchanging data with the validation-service. Not all validation-service may support this option, this should be verified with the service documentation or maintainer.
- Target endpoint Define the complete URL to the web-service endpoint (required). For example
- Specific to System services types
- Path to the binary In case the service is an executable on the Unix server hosting EVSClient
application, then provide the path to the executable (required). For example
/usr/local/bin/myservice.
- Path to the binary In case the service is an executable on the Unix server hosting EVSClient
application, then provide the path to the executable (required). For example
- Is available ? Enable or Disable this service. Disabled services will not be displayed in validation GUI and cannot be contacted through the web-service API. This option can be convenient for configuration maintenance, administrator may then prepare configurations without disturbing the running system.
Click on the save button once the configuraiton is input.
The next step is to associate referenced-standards to the newly created services to give context and help the user in its validation process.
References to standards
A referenced-standard in EVSClient is a classification of validation and validation-service. This classification should reflect the underlying standard, specification or IHE integration-profile to help the user to find which validator he/she must select to validate a document. In practice, referenced-standards are entries in the drop-down menu bar and can be associated to one or more validation-services.
Note that a pre-defined list of standard names is available and matches the standard for which a validation service client has been implemented within the tool.
Users with the administrator role can access this section of the tool to configure the standards from Administration –> Manage referenced standards menu entry. The page lists the standards already defined within the tool. Users can edit existing entries or add new ones.
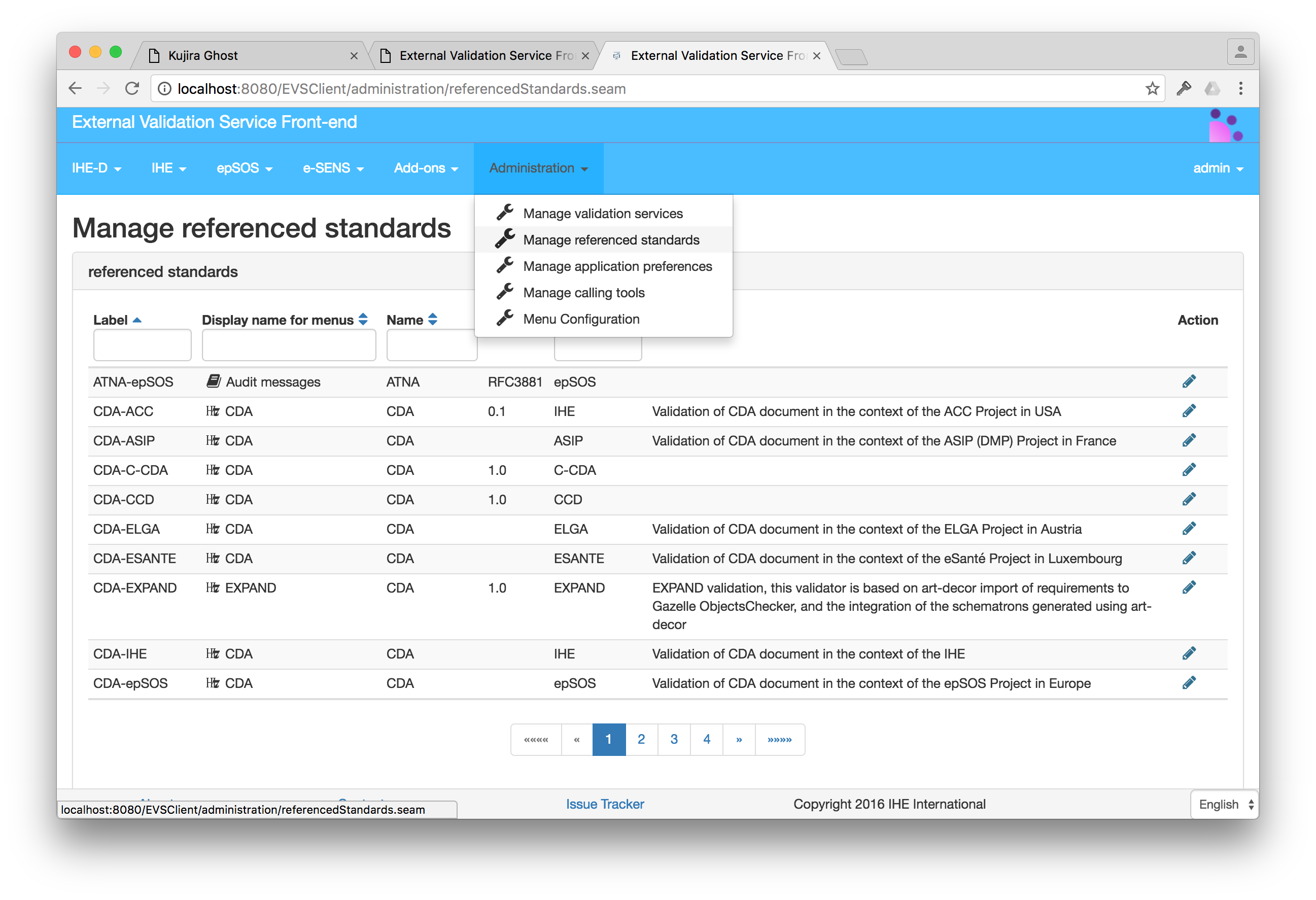
Add or edit a referenced standard
A referenced standard is defined by a name, a type of validation, an optional validator-filter, a description, an icon and a optional list of stylesheet.
- The name must be unique and will be displayed in EVS menus for user orientation.
- The type of validation will be used as category for documents and validation-reports storage (but also in remote-validation).
- The validator-filter will be used to filter-out validator entries in validate web page. This filtering is mainly used to present a limited list of validator that are more suitable for the desired scope of this referenced-standard.
- The description (html content) will be display on the validate web page, and can be used to give detail on the validation procedure in the context of this reference-standard.
- The icon is used to customize the drop-down entry menu (Icons class are
font-awesome names such as
fa fa-book, other can be found at font-awesome v4). - For XML Documents, a list of XML stylesheets can be provided to nicely display the content of the validated document to the user.
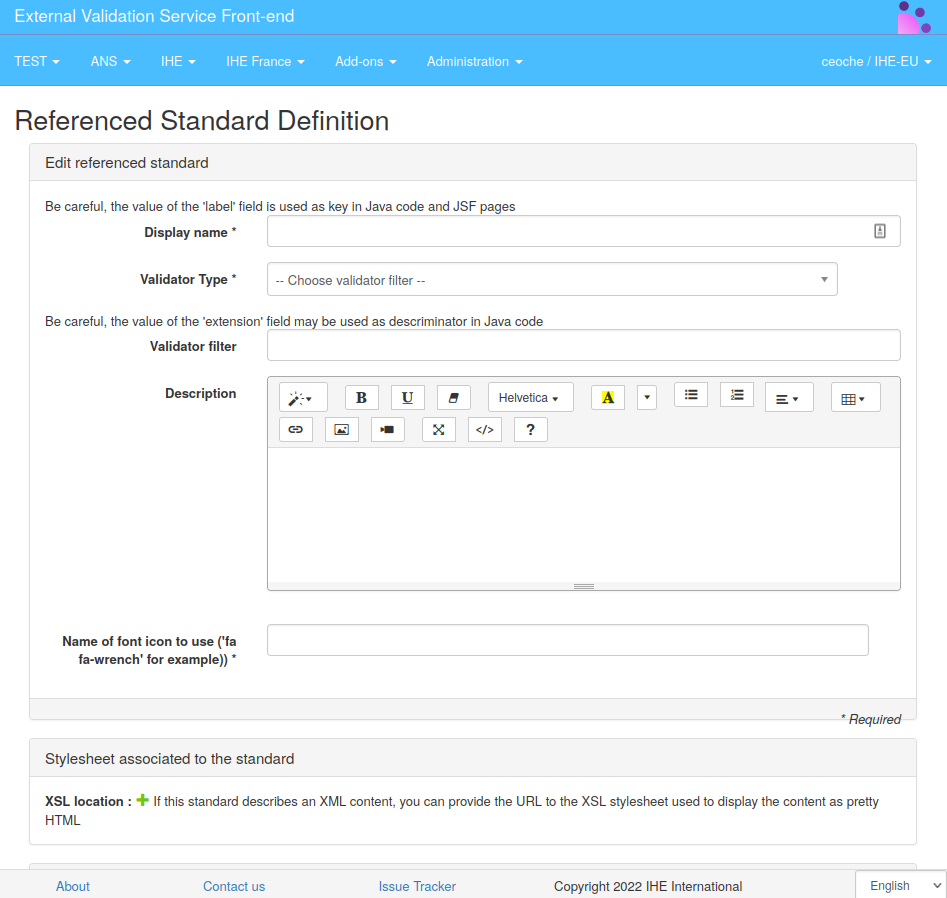
Referenced-standard must be associated with at least one validation-service.
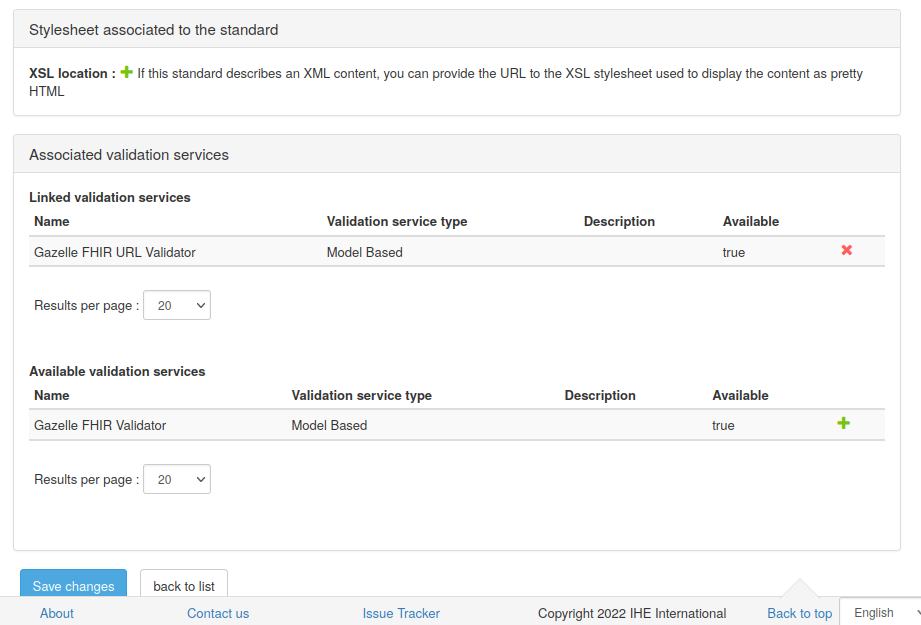
Validation-services associated and presented in the context of this referenced-standard will have their validator list filtered-out according to the validator-filter of this referenced-standard.
Configuring the top bar menu
A menu bar is made of two kinds of entities, the menu groups which are the menu entries displayed in the top bar and the menu entries which are the entries displayed in the drop-down list. The top bar menu of EVSClient is built using a list of menu groups stored in the database. Administrator users can update this list from the page accessible at Administration –> Menu configuration. On this page are listed all the menu groups defined for this instance of the tool.
A menu group is defined by:
- a label
- the list of referenced standards accessible from this menu group (they define the sub-menu entries).
- a Is available ? option to enabled/disable the menu group in the GUI.
For each standard listed in the menu group, the icon will be the one defined at standard level. For each menu (except for DICOM one), the sub menus will be “validate”, “validation logs” and “statistics”. Links to these sections are automatically built from the standard name and extension.
The order of the Menu on the top bar is modifiable from the Menu configuration table.
Calling tools
Other tools of the Gazelle-Test-Bed that are able to send validation of documents to EVSClient and through the web GUI are called Calling tools. They can upload documents or ressource to validate onto EVSClient and redirect the user towards EVSClient GUI for him/her to complete the validation process. Once the validation is done, EVSClient can redirect back the user to the calling tool and return the validation results.
All of those calling tools need be registered in EVS in order to maintain document ids mapping and define URL redirections. The registration list is accessible under Administration –> Calling tools.

It is possible to add a calling tool by clicking on the “Register a new tool” button or edit an existing one by clicking on the field to modified directly in the table.
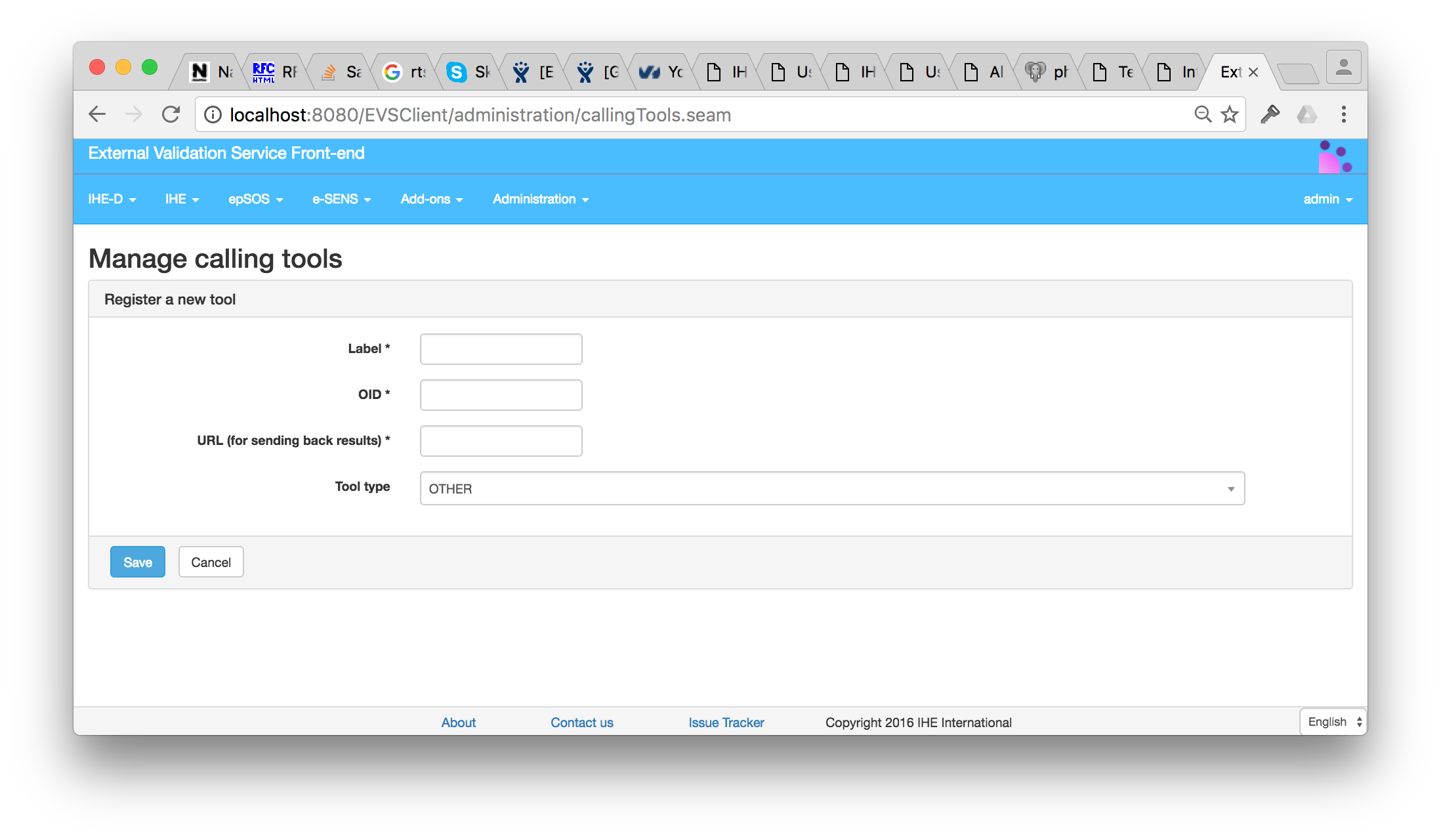
Each tool requires
- a Label for helping administrator distinguish calling tools.
- an OID which uniquely identifies the instance of the tool.
- the URL used to send back results and redirect the user to the calling-tool GUI.
- the tool type that defines which application is calling. This list represent 3 types of
data-exchange procedures that have been implemented in EVSClient over time:
- PROXY, For Gazelle Proxy that is using specific proxyType parameters.
- TM For Gazelle Test Management that is sending two different types of documents and
is handling identifiers differently. - OTHER, for other applications, that follow the default data-exchange procedure.
URL and Tool type fields depends on application implementation. Please refere to the documentation of each tool you need to registered to get the right values.
EVSClient setup to keep EVS 5.x.x legacy data.
When updating EVSClient from 5.x.x to 6.x.x, previous validation data will be lost because of the non-compatible database schema.
However there is a setup in EVS 6.x.x to co-exist with an EVS 5.13.8 (or newer 5.x.x) that is switch in read-only and used to archive previous validation results. This setup will prevent any data lost, validation results are still browsable by users and calling tools can still display status and permanent link to get detailed results of those archived results.
To setup this work-around, follow this procedure :
In the EVSClient 5.x.x you want to keep as archive for previous validation-results,
- set application preference
validation_enabledtofalse - restart EVSClient 5.
In the EVSClient 6.x.x,
- set application preference
legacy_results_redirection_enabledtotrue. - set application preference
legacy_results_evs_urlto the URL of EVSClient 5.x.x (examplehttps://mydomain.org/EVSClient/). - add all calling tools that were previously registered in EVSClient 5.x.x (See Calling tools administration).
- restart EVSClient 6.
Then repeat for all calling-tool registered:
- Set EVSClient URL in application preferences of the calling tool to the URL of EVSClient 6.x.x
(example
https://mydomain.org/evs/). - Restart the calling tool.
Dicom validator installation
Dicom3Tools
If a DICOM validation is wished, then Dicom3Tools needs to be installed on the host machine.
The following instructions are for a linux system based on the apt package system. Any other distribution may find instructions for installation of the tool from David Clunie (https://www.dclunie.com/dicom3tools.html). This is not the scope of this document to provide installation instructions for all platforms.
sudo apt-get install g++
sudo apt-get install xutils-dev man-db
Download the last Dicom3tools version here and untar it.
Go in the untar folder.
./Configure
imake -I./config
make World
make install
make install.man
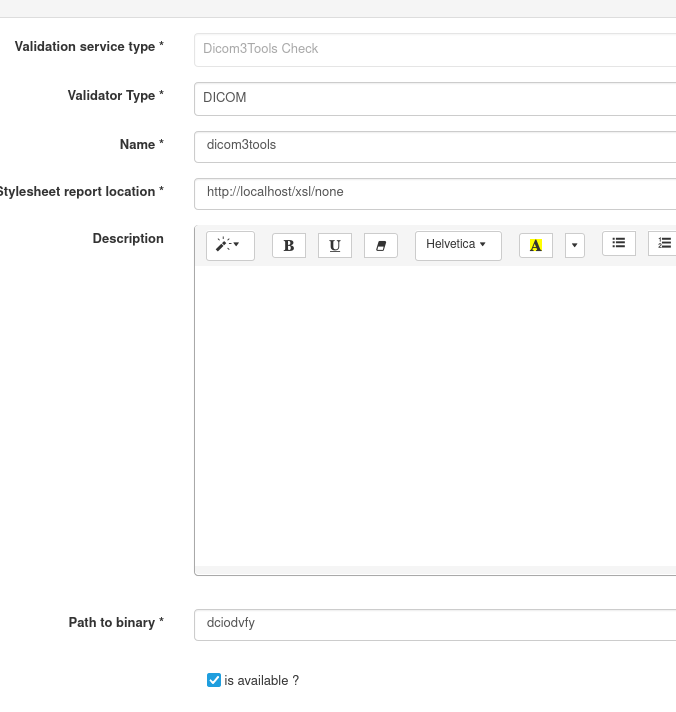
In EVSClient, the validation service must be configured as follows:
Pixelmed
OUT DATED Documentation to review Not yet re-integrated in EVS 6.0.0.
Build and install
- Launch a build of http://gazelle.ihe.net/jenkins/job/Pixelmed-jar/
- Download Pixelmed-jar-x.x.x-script.zip ( example : http://gazelle.ihe.net/jenkins/job/Pixelmed-jar/ws/target/Pixelmed-jar-1.0.1-SNAPSHOT-script.zip)
sudo mkdir /opt/pixelmed
sudo chown gazelle:jboss-admin /opt/pixelmed/
- unzip it in /opt/pixelmed/
- edit /opt/pixelmed/bin/pixelmedValidator.sh, add JAVA_HOME={path to java 7 home}
Upload new jar in nexus
- Download the last Pixelmed version here
- Logged on to http://gazelle.ihe.net/nexus/index.html#view-repositories;thirdparty~browseindex
- Create a pom like this :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.pixelmed</groupId>
<artifactId>dicom</artifactId>
<version>20140326</version>
</dependency>
- Click on “Artifact upload”
- Select GAV definition : From POM
- Select your new pom to upload it
- Add artifacts : sourceFiles.jar and executable.jar
- To finish click on upload artifacts
You can now get your new dependency in the project http://gazelle.ihe.net/jenkins/job/Pixelmed-jar/ , do the build and install.
EVS API
EVSClient API documentation is available at https://app.swaggerhub.com/apis-docs/gazelletestbed/gazelle-evs_client_api/3.0#/